Convert Docbook To Pdf Windows 8
Bosch pst 52a manual dexterity review. DocBook.dbk,.xmlapplication/docbook+xmlDeveloped byType of formatExtended from,?YesDocBook is a for technical. It was originally intended for writing technical documents related to computer hardware and software but it can be used for any other sort of documentation.As a semantic language, DocBook enables its users to create that captures the logical structure of the content; that content can then be published in a variety of formats, including, and, without requiring users to make any changes to the source. In other words, when a document is written in DocBook format it becomes easily portable into other formats, rather than needing to be rewritten. Contents.Design DocBook is an language. In its current version (5.x), DocBook's language is formally defined by a with integrated rules. (There are also +Schematron and (DTD) versions of the schema available, but these are considered non-standard.)As a semantic language, DocBook documents do not describe what their contents 'look like', but rather the meaning of those contents.
For example, rather than explaining how the for an article might be visually formatted, DocBook simply says that a particular section is an abstract. It is up to an external processing tool or application to decide where on a page the abstract should go and what it should look like or whether or not it should be included in the final output at all.DocBook provides a vast number of semantic element tags. They are divided into three broad categories: structural, block-level, and inline.Structural tags specify broad characteristics of their contents.
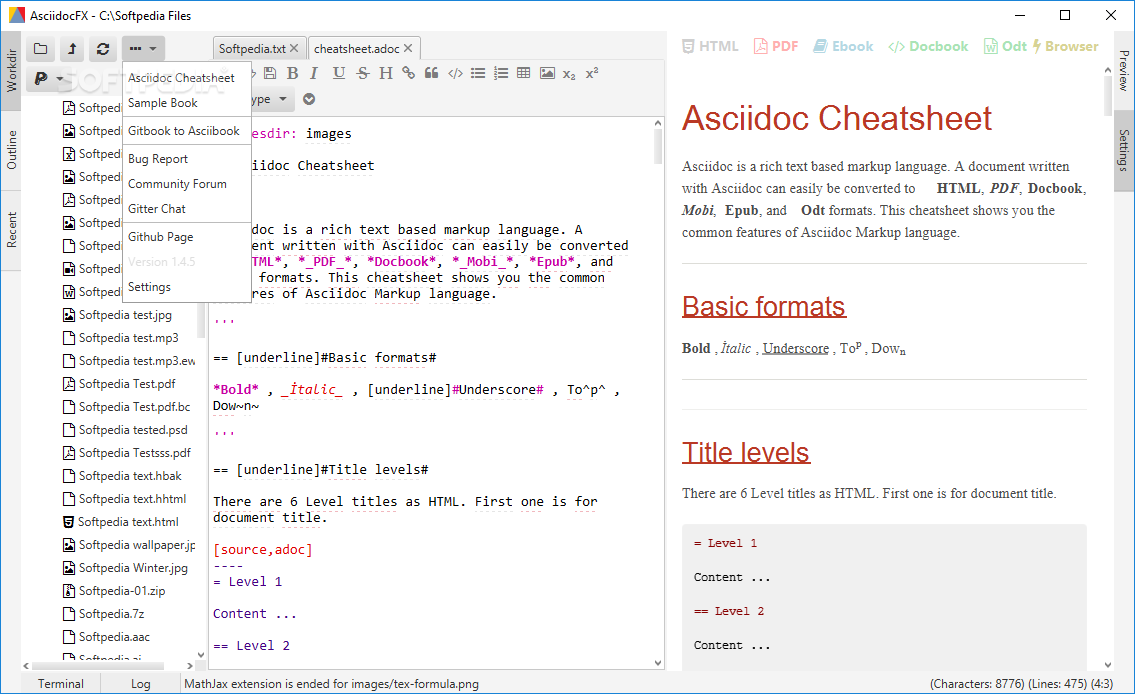
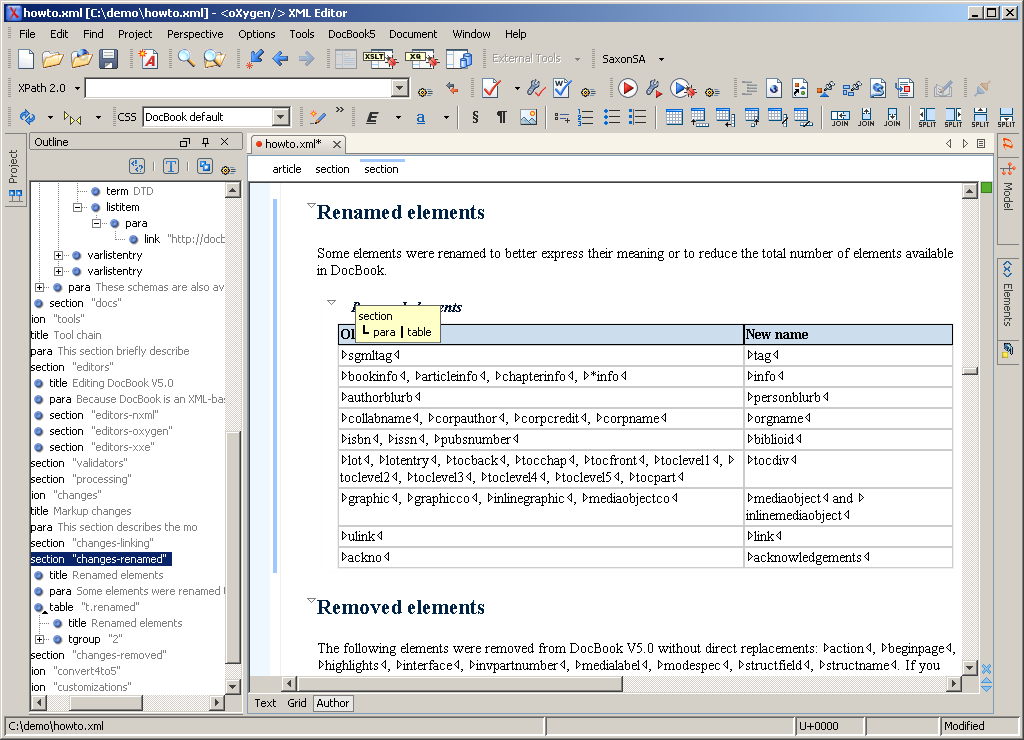
PDF to Excel Converter for Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7 lets you converter PDF files to Microsoft Excel for further. Need to convert PDF to Microsoft Excel for. This tutorial explains how to write DocBook files in Eclipse and how to convert these files into various output formats, e.g., to HTML and PDF.
The book element, for example, specifies that its child elements represent the parts of a book. This includes a title, chapters, glossaries, appendices, and so on.
Very simple book Chapter 1 Hello world! I hope that your day is proceeding splendidly! Chapter 2 Hello again, world! Semantically, this document is a 'book', with a 'title', that contains two 'chapters' each with their own 'titles'. Those 'chapters' contain 'paragraphs' that have text in them. The markup is fairly readable in English.In more detail, the root element of the document is book. All DocBook elements are in an, so the root element has an xmlns attribute to set the current namespace.
Also, the root element of a DocBook document must have a version that specifies the version of the format that the document is built on.(XML documents can include elements from multiple namespaces at once. For simplicity, the example does not illustrate this.)A book element must contain a title, or an info element containing a title. This must be before any child structural elements. Following the title are the structural children, in this case, two chapter elements. Each of these must have a title.
They contain para block elements, which can contain free text and other inline elements like the emphasis in the second paragraph of the first chapter.Schemas and validation Rules are formally defined in the DocBook. Appropriate programming tools can validate an XML document (DocBook or otherwise), against its corresponding schema, to determine if (and where) the document fails to conform to that schema. XML editing tools can also use schema information to avoid creating non-conforming documents in the first place.Authoring and processing Because DocBook is XML, documents can be created and edited with any text editor. A dedicated is likewise a functional DocBook editor. DocBook provides for popular XML schema languages, so any XML editor that can provide content completion based on a schema can do so for DocBook. Many or come with the ability to edit DocBook like a.
Because DocBook conforms to a well-defined XML schema, documents can be validated and processed using any tool or programming language that includes XML support.History DocBook began in 1991 in discussion groups on and eventually became a joint project of and and eventually spawned its own maintenance organization (the Davenport Group) before moving in 1998 to the SGML Open consortium, which subsequently became. DocBook is currently maintained by the DocBook Technical Committee at OASIS.DocBook is available in both and forms, as a. And forms of the XML version are available. Starting with DocBook 5, the RELAX NG version is the 'normative' form from which the other formats are generated.DocBook originally started out as an SGML application, but an equivalent XML application was developed and has now replaced the one for most uses. (Starting with version 4 of the SGML DTD, the XML DTD continued with this version numbering scheme.) Initially, a key group of software companies used DocBook since their representatives were involved in its initial design. Eventually, however, DocBook was adopted by the open source community where it has become a standard for creating documentation for many projects, including, desktop documentation, the references, the documentation, and the work of the.Pre DocBook v5.0 Until DocBook 5, DocBook was defined normatively by a Document Type Definition (DTD).
Because DocBook was built originally as an application of, the DTD was the only available schema language. DocBook 4.x formats can be SGML or XML, but the XML version does not have its own namespace.DocBook 4.x formats had to live within the restrictions of being defined by a DTD. The most significant restriction was that an element name uniquely defines its possible contents. That is, an element named info must contain the same information no matter where it is in the DocBook file.
As such, there are many kinds of info elements in DocBook 4.x: bookinfo, chapterinfo, etc. Each has a slightly different content model, but they do share some of their content model. Additionally, they repeat context information. The book's info element is that, because it is a direct child of the book; it does not need to be named specially for a human reader. However, because the format was defined by a DTD, it did have to be named as such.
The root element does not have or need a version, as the version is built into the DTD declaration at the top of a pre-DocBook 5 document.DocBook 4.x documents are not compatible with DocBook 5, but can be converted into DocBook 5 documents via an XSLT stylesheet. One ( db4-upgrade.xsl) is provided as part of the distribution of the DocBook 5 schema and specification package. Output formats DocBook files are used to prepare output files in a wide variety of formats. Nearly always, this is accomplished using stylesheets.
These are stylesheets that transform DocBook documents into a number of formats (, for later conversion into, etc.). These stylesheets can be sophisticated enough to generate tables of contents, glossaries, and indexes. They can oversee the selection of particular designated portions of a master document to produce different versions of the same document (such as a 'tutorial' or a 'quick-reference guide', where each of these consist of a subset of the material). Users can write their own customized stylesheets or even a full-fledged program to process the DocBook into an appropriate output format as their needs dictate.Norman Walsh and the DocBook Project development team maintain the key application for producing output from DocBook source documents: A set of stylesheets (as well as a legacy set of stylesheets) that can generate high-quality and print (/) output, as well as output in other formats, including, and HTML Help.is a chunked HTML output format in the stylesheets that was introduced in version 1.76.1. The documentation for web help also provides an example of web help and is part of the DocBook XSL distribution.The major features are its fully CSS-based page layout, search of the help content, and a table of contents in collapsible-tree form.
Search has, match highlighting, explicit page-scoring, and the standard multilingual. The search and TOC are in a pane that appears as a, but is actually implemented with and cookies (so that it is progressive).Simplified DocBook DocBook offers a large number of features that may be overwhelming to a new user. For those who want the convenience of DocBook without a steep learning curve, Simplified DocBook was designed.
It is a small subset of DocBook designed for single documents such as articles or white papers (i.e., 'books' are not supported). The Simplified DocBook DTD is currently at version 1.1. See also.References. Norman Walsh (June 2010). O'Reilly Associates.
Docbook Reader
Bob Stayton (2005). Sagehill Enterprises. Joe Brockmeier (2001).
DocBook Publishing — A Better Way to Create Professional Documents. Prima Tech's Linux Series.External links. Collection of DocBook information, including a 4.x and 5.0 version of DocBook: The Definitive Guide and all versions of the DocBook schemas/DTDs. Normative home of DocBook schema/DTD.
at. Fully bookmarked PDF of the Guide for DocBook 3.x and 4.x.
As I understand it, DocBook is usually only written and edited. It is then processed into a different format (Postscript, HTML & c.) for distribution and reading. Latex is generally handled the same way, compare also compiling source code into computer programs before use.Nonetheless, promises to be a graphical editor for DocBook.
It's available for many platforms. I have never used it for DocBook, but for Latex it works well unless you want to edit a complex existing document. This is an unfortunate problem inherent to creating software that needs to parse an extensible language.
Lyx also tends to not preserve parts and aspects of the source file that don't affect the output, which can surprise and/or aggravate other persons, but this is irrelevant if you just want to read files.